Laketown "Miwa no Mori"
Exterior Thermal Ventilation Wall
 |
|||
| Exterior Thermal Ventilation Wall | |||
 |
|||
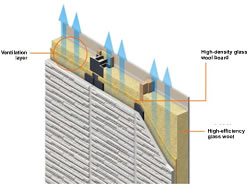
Outer walls are constructed with heat insulation, making maximum use of the respective merits of filling heat insulation and external heat insulation. For the former, we make effective use of spaces in the middle of thick walls, which we fill with heat insulation material (high-efficiency glass wool). For the latter, we surround the whole exterior of the building with heat insulation material (high-density glass wool boards) to protect the steel frame pillars that can become thermal weak points. Since these materials are factory-produced under rigorous conditions of quality management, they are especially characterized by constant levels of quality and high precision.
Externally attached roll-up screens
 |
|||
| Externally attached roll-up screens | |||
 |
 |
||
Externally attached roll-up screens serve to block strong summer sunlight and western sunlight outside the windows. About 70% of sunlight heat entering via windows can be eliminated in this way, and greater sunlight screening effects can be achieved than when hanging curtains or blinds inside the room. The screens can be rolled up and stored above the windows when not in use, offering easy control of both sunlight intake and screening.
Wind status / heat environment simulation
 |
|||
| Summer morning winds (east-northeasterly) | |||
 |
 |
 |
|
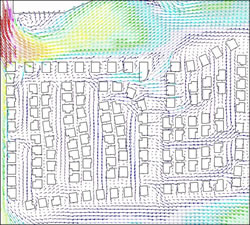
The properties of winds blowing in the construction area (Koshigaya City) are analyzed from the Meteorological Agency’s AMeDAS data for each season. Then, with the cooperation of the Kato and Ooka Research Laboratories at the Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo, wind status and heat environment simulations are carried out with the scheduled buildings and plants arranged in the district in question, and the flow of wind in the area is analyzed.
Wind direction analysis for each housing unit
 |
|||
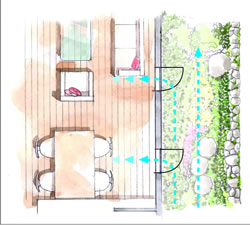
| Wind catcher window leads fresh air into the home | |||
 |
 |
||
Based on the analysis results of the wind status and heat environment simulations, elevation plans are drawn up for each house in the area, as well as the arrangement of openings, plants, etc. These are then designed to ensure an efficient intake of fresh air inside the house. Wind environment simulation is carried out for each house, the air course inside the house is confirmed, and the position of windows, etc., is adjusted if there is a problem. The result of this process is that better air courses are planned. From the simulation results, meanwhile, we propose methods of successfully incorporating fresh air into homes, for the benefit of the residents. We do so by indicating how winds can be used for ventilation as well as effective ways of opening windows in each housing unit, according to the season and daily hours of use.
Eco Navigator
 |
|||
| Example of proposal screen | |||
 |
|||
This is our original energy simulation software that can calculate the heat loss coefficient (Q value), annual energy consumption, light and heat consumption and CO2 emissions of a house, by merely inputting details such as the building data, construction site, family composition and items of equipment. The software can also calculate building maintenance costs over 30 years and compare running costs resulting from the introduction of energy-saving equipment. This makes it possible to grasp or study “environmental merits” and “economic merits” from the time of purchasing the house into the future. This software won the Prize of Excellence in the “9th Green Purchasing Awards” hosted by the Green Purchasing Network.
Ryonabi
 |
|||
| Ryonabi | |||
 |
 |
 |
|
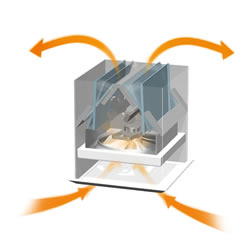
Our original heat exhaust system, which uses natural forces to emit hot air into the loft space above the uppermost floor and thereby relieve heat in the rooms. An actuator that expands and contracts according to changes in temperature switches a damper on or off, thereby automatically controlling the indoor environment in line with the season. In early summer, it uses the natural force whereby warm air rises to emit hot air from inside the room, in full summer it automatically operates a fan that forcibly expels air, and in winter it closes the damper to prevent the intrusion of cool air. Though not installed in these houses, it is used in other homes inside the condominium area.
Previous Building |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Next Building Next Building |
CASBEE is a method for rating the environmental performance of buildings using Building Environmental Efficiency (BEE) as an indicator, which is based on the results of separate scores obtained for Q-1~Q-3 (Quality) and LR-1~LR-3 (Load Reduction).







 | Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.